Human brainstem-thalamus posterior view description
John A Beal, PhD
Dep't. of Cellular Biology & Anatomy, Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center ShreveportHuman brainstem and thalamus - posterior view
- Taenia choroidea (and lateral: Lamina affixa, Stria terminalis)
- Thalamus, Pulvinar thalami
- (Ventriculus tertius)
- Stalk of Glandula pinealis
- Habenula
- Stria medullaris
- Colliculus superior
- Brachium colliculi superioris
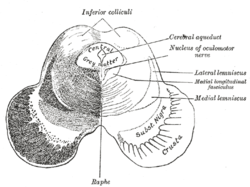
- Colliculus inferior
- Brachium colliculi inferioris
- Corpus geniculatum mediale
- Sulcus medianus
- Pedunculus cerebellaris superior
- Pedunculus cerebellaris inferior
- Pedunculus cerebellaris medius
- Tuberculum anterius thalami
- Obex, Area postrema
A: Thalamus, B: Mesencephalon, C: Pons, D: Medulla oblongata
On this specimen, the following thalamic structures can be seen: 1. the Epithalamus (Stria Medullaris Thalami, Habenula, & Pineal), 2. the Anterior Nucleus of the dorsal thalamus (Anterior Tubercle) and, 3. the Pulvinar (the large posterior portion of the dorsal thalamus which overhangs the midbrain.
The Medulla, Pons & Midbrain are delineated on the posterior surface of the brainstem.
NOTE: The 4 Colliculi of the tectum are refered to collectively as the Quadrigeminal Plate.
The three Cerebellar Peduncles are shown here as they enter the brainstem on each side. In the Midbrain identify the Superior Colliculus and Inferior Colliculus. Also identify the Brachium of the Superior Colliculus and the Brachium of the Inferior Colliculus which connect with the Lateral Geniculate Body and Medial Geniculate Body, respectively.
The cerebellum forms the roof of the 4th ventricle and is connected to the brainstem by 3 pairs of peduncles or pillars (shown on right side of brainstem) . The peduncles are made up of axons entering and leaving the cerebellum. The Inferior Cerebellar peduncle projects from the medulla, the large Middle Cerebellar Peduncle projects from the Pons, and the Superior Cerebellar Peduncle connects with the midbrain.
Relevantní obrázky
Relevantní články
Prodloužená míchaProdloužená mícha je část centrální nervové soustavy obratlovců, která je spojovacím článkem centrální nervové soustavy mezi koncovým mozkem a páteřní míchou. Stavbou se částečně podobá páteřní míše, ale zanořuje se do ní řada struktur zadního a středního mozku. Evolučně představuje nejstarší část mozku. .. pokračovat ve čtení
ThalamusThalamus je spolu s epithalamem součástí zadní části mezimozku (diencephalon) a je seskupením senzorických, asociačních a nespecifických jader. Zprostředkovává převod informací přicházejících z periférie do specifických projekčních a asociačních oblastí mozkové kůry a do důležitých center mozečku. Umožňuje také vzájemnou interakci vyšších oddílů CNS. .. pokračovat ve čtení
Střední mozekStřední mozek je oddíl centrální nervové soustavy, který umožňuje zprostředkování důležitých reflexů a procházejí jím dráhy, které vedou signály z páteřní míchy do mozečku a mozkové kůry, a také vzruchy opačným směrem z mozkové kůry a bazálních ganglií do mozečku, prodloužené a páteřní míchy. .. pokračovat ve čtení